Sustainability entails fulfilling current endeavours without sacrificing the potential for future fulfillment by others. In the dynamic and ever-evolving landscape of modern business, a new paradigm has emerged, redefining success beyond the confines of profits and shareholder value.
This paradigm, known as corporate sustainability, has swiftly become a guiding principle for companies seeking not only financial prosperity but also a positive impact on the environment and society. Corporate sustainability transcends mere rhetoric; it embodies a strategic blueprint beyond the pursuit of short-lived gains; elevating enterprises towards enduring triumph while concurrently nurturing a positive footprint on both the global ecosystem and society at large.
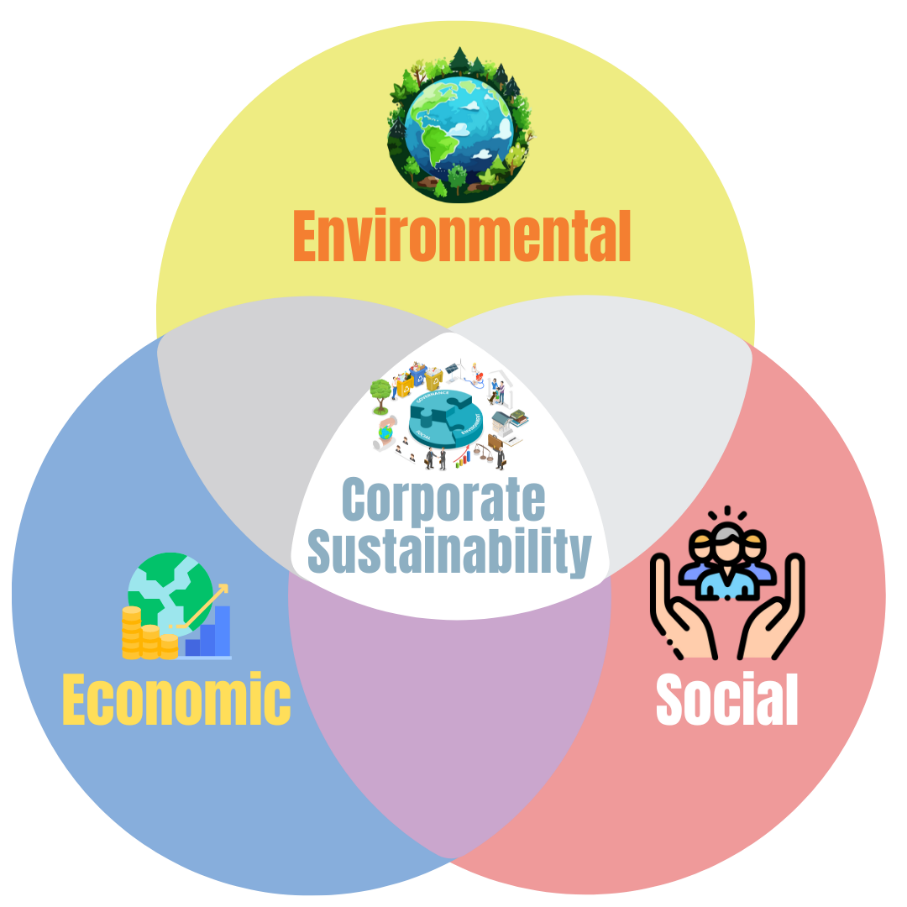
What is Corporate Sustainability?
Corporate sustainability in simple terms entails doing business that centres on environmental concerns, social obligations, and economic factors while concurrently generating enduring, value-driven outcomes for shareholders, staff, customers, and the broader community. Corporate sustainability frequently aligns with the principles encompassed by ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance). These components collectively serve as the crucial criteria through which companies assess the environmental effectiveness and enduring sustainability of their operations
At its very essence, the foundation of corporate sustainability is upheld by three interwoven pillars: environmental consciousness, social responsibility, and economic resilience. The fundamental aspects of corporate sustainability are rooted in the three themes of economic, environmental, and social standpoints. Let’s now delve into each of these pillars and elucidate why harmony is pivotal in cultivating a durable and ethically accountable business model.
- Environmental Sustainability: Guardians of the Planet
The environmental pillar deals with the impact a business operation has on the environment. With growing concerns about climate change, pollution, and resource depletion, companies are under increasing pressure to channel operations, facilities, and investments in a way that minimizes negative impacts on the environment. It encompasses a range of practices and initiatives aimed at reducing carbon emissions, conserving natural resources, and protecting ecosystems. With the following action points, this pillar tends to get the most attention from most companies.
Carbon footprint reduction: The carbon footprint of human activities is severalfold. Adopting practices that reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate the adverse effects of climate change is a central aspect of environmental sustainability. Companies are adopting strategies to reduce their carbon footprint, which includes transitioning to renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency, and implementing sustainable transportation solutions. To achieve this, companies must be willing to invest in alternative energy sources like solar power installations, optimize manufacturing processes, and adopt operation approaches that help lower greenhouse gas emissions.
Resource conservation: This involves embracing business practices that foster the sustainability and effective management of both renewable and non-renewable natural resources. It encompasses energy preservation, efficient solid waste handling, optimizing water usage, recycling initiatives, conservation of natural areas, safeguarding of cultural and historical resources, and adopting circular economy practices. By designing products with recyclability in mind and incorporating recycled materials, businesses are closing the loop on resource consumption and waste generation.
Biodiversity preservation: The loss of biodiversity stands as an urgent global concern, and corporate sustainability endeavours encompass the safeguarding of natural habitats and the endorsement of biodiversity conservation initiatives. As companies intensify their focus on environmentally responsible practices, they are directing investments toward actions that shield ecosystems and bolster the well-being of indigenous plant and animal life. It is imperative to prioritize the preservation of distinctive ecosystems and optimize resource utilization. Preventing poaching and wildlife hunting remains crucial. Equally significant is the meticulous development of reserves and protected regions, ensuring they contribute harmoniously to the overall conservation effort.
- Social Sustainability: Nurturing People and Communities
Beyond environmental considerations, social sustainability recognizes the significance of fostering fair labour practices, diversity and inclusion, and community engagement. A company’s relationship with its employees, customers, suppliers, and the communities it operates in plays a pivotal role in its long-term success.
Ethical labour practices: Ethical labour practices encompass work ethics that adhere to legality, fairness, and the provision of proper treatment for the workforce. This entails creating conditions that prevent physical or psychological harm to employees. These practices are intentionally crafted to embody morality, ethics, and transparency, with a primary focus on upholding workers’ human rights. The ethical treatment of employees entails surpassing the bare legal requirements, potentially entailing actions such as offering a living wage or demonstrating dedication to the training and advancement of the workforce.
Diversity and inclusion: Diversity and inclusion constitute integral facets of corporate sustainability. A workplace characterized by diversity has the potential to enhance a company’s economic advantage, cultivate a reputable brand identity, and play a role in the enduring health of the environment. Furthermore, the significance of diversity and inclusion extends to fostering equity within society, promoting an inclusive work environment, and fostering economic well-being. Companies are recognizing the value of diverse perspectives and are actively working to eliminate biases, promote gender equality, and create opportunities for underrepresented groups.
Community engagement: A socially responsible company transcends mere financial considerations and actively engages in enhancing the welfare of the communities it functions within. This commitment might encompass backing local education, healthcare, and infrastructure initiatives, in addition to addressing community requirements during periods of adversity.
- Economic Sustainability: Prosperity for the Long Term
The economic dimension pertains to a company’s financial viability. It entails cultivating enduring value for shareholders, employees, consumers, and society through the pursuit of conscientious environmental, social, and governance approaches. An economically sustainable company exemplifies ethical practices, possesses a well-defined mission, and demonstrates transparent dedication to accomplishing its objectives. A company must maintain financial viability to continue its sustainability journey and make meaningful contributions to the planet and society.
Long-term profitability: This refers to sustainable financial returns over an extended timeframe, while maintaining equilibrium between profitability and social as well as environmental responsibility. The significance of long-term profitability lies in its capacity to ensure the continuous functioning of businesses, thereby engendering value for shareholders, employees, and the broader society. To achieve this, businesses often employ sustainable practices like ethically sourcing materials, curtailing energy consumption, and optimizing shipping methods. However, achieving the equilibrium between immediate profits and long-term sustainability presents a challenge to companies, necessitating strategic choices that effectively harmonize shareholder interests with broader demands.
Innovation and adaptability: Thriving in a dynamic business landscape necessitates an ongoing commitment to innovation and adaptability. Companies committed to sustainability place emphasis on the advancement and exploration of environmentally conscious products, technologies, and methodologies. These not only cater to consumer needs but also resonate with values associated with the environment and society.
Stakeholder engagement: Nurturing robust connections with stakeholders such as investors, customers, employees, and communities plays a pivotal role in achieving economic sustainability. Through transparent communication and fulfilling the diverse expectations of stakeholders, businesses establish a firm social foundation for their operations and enhance their appeal to potential investments.
In conclusion, corporate sustainability transcends the pursuit of excellence in a singular pillar while disregarding the rest. The true strength of this paradigm emerges from the seamless amalgamation of environmental, social, and economic considerations. By harmonizing these three pillars, businesses initiate a virtuous cycle of conscientious growth that not only enhances their own financial standing but also contributes positively to the environment and society on a broader scale.
Found it interesting and would like more in the mail?




