Throughout history, wildfires have been a prevalent natural disaster, wreaking havoc on both ecosystems and human settlements. Recently, a heatwave and wildfires in parts of the Northern Hemisphere led to record-breaking temperatures across the globe. A few days ago, the BBC reported the evacuation of approximately 1,200 children near a Greek seaside resort. Adding to the severity of the recent high temperatures is an anticyclone known as the ‘Cerberus heatwave,’ named by the Italian Meteorological Society after the three-headed monster depicted in Dante’s Inferno. This heatwave is expected to bring even more extreme weather conditions in the near future as the United Nations recently verified a European heat record of 48.8°C set in Sicily back in 2021. Understanding the factors that contribute to wildfire spread and intensity is crucial in developing effective strategies to mitigate their impact.
The causality factors
Wildfires can be triggered by both natural and human causes. Natural causes include lightning strikes, volcanic eruptions, and spontaneous combustion. Human-caused wildfires, however, account for the majority of fire incidents and are often a result of human activities. The Cerberus Heatwave results from a complex interplay of atmospheric factors, with climate change acting as a potent catalyst. Here are the primary causes contributing to its formation:
Anticyclone formation: The presence of a dominant high-pressure system known as an anticyclone, according to scientists, is the primary factor responsible for the formation of the Cerberus Fire. The air pressure at the surface of an anticyclone is higher than the air pressure above it, causing the air above it to descend. Because there is more atmosphere above, the pressure rises as the air descends, and as a result, the temperature rises as well. This results in the formation of a heat dome, which acts as a thermal barrier, preventing heat from dissipating and causing temperatures to rapidly rise. This trapped warm air condenses at the surface, making the environment oppressive and interfering with natural cooling mechanisms. As a result, temperatures skyrocket, allowing the ferocious Cerberus Fire to wreak havoc.
Oceanic Influences: Oceanic influences are critical in shaping heat waves such as the infamous Cerberus Fire. The temperature of the surrounding oceans has a direct impact on atmospheric conditions, either intensifying or mitigating the effects of heat waves. Not long, the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) warned against a potentially devastating ocean temperature phenomenon, called El Niño, a global weather phenomenon caused by a significant temperature surge in the Pacific Ocean. El Niño causes climatic events all over the world, raising ocean temperatures and releasing significant heat into the atmosphere. This oceanic warming has far-reaching consequences, influencing a variety of weather changes, including exacerbating occurrences like the Cerberus Heatwave, resulting in record-breaking temperatures and wildfires.
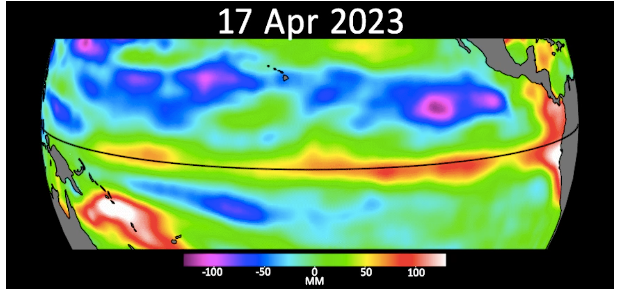
Source: NASA/JPL-Caltech– This picture shows a live wave, called Kelvin waves, moving warm water across the equatorial Pacific Ocean from west to east during March and April. The signals can be an early sign of a developing El Niño and were detected by the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich sea level satellite
Climate change and the Cerberus heatwave
Climate change plays a significant role in the occurrence and severity of extreme weather events, and the Cerberus Heatwave only exemplifies this environmental impact. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) research establishes a direct link between rising temperatures and altered atmospheric circulation, leading to more frequent extreme temperatures. One major consequence of climate change is its influence on wildfires. Notably, between 1984 and 2015, climate change is purported to have increased the occurrences of wildfires. Several factors, such as temperature, soil moisture, and the presence of potential fuel sources like trees and shrubs, all contribute to wildfire risk. Studies find that increasing temperatures worsen the hot and dry conditions that contribute to wildfire ignition and rapid spread. This is because an increase in temperatures causes greater evaporation, drying out vegetation and making it prone to igniting, turning leaf litter and fallen branches into combustible material. Notably, Climate change also intensifies the drying of organic matter in forests, fueling wildfires. As such, as global temperatures rise, the size, frequency, and severity of wildfires are expected to escalate in the future.
Mitigating the heatwaves
To mitigate the impact of Cerberus Heatwave on wildfires, proactive steps need to be taken at various levels. A few things that stakeholders can do include:
Mitigation of Climate Change: Addressing the underlying cause of the Cerberus Heatwave requires an unwavering commitment to climate change mitigation. Reducing greenhouse gas emissions through sustainable practices, transitioning to renewable energy sources, and enacting environmentally friendly policies are essential measures to combat global warming. Governments, businesses, and individuals must work together to reduce carbon emissions and preserve the delicate balance of our planet’s climate.
Early Warning Systems: Wildfires can be greatly reduced with the help of early detection and warning systems. Satellites, drones, and specialized sensors are all examples of cutting-edge technologies that can aid in the early detection of wildfires. Communities and first responders can better prepare for and respond to a fire if they receive timely alerts. Wildfire response can be greatly enhanced and lives saved if such systems are integrated into the existing infrastructure.
Ecosystem Preservation and Sustainable Land Management: Ecosystem preservation and restoration can act as a defense against the devastating effects of the Cerberus Heatwave. Reforestation, afforestation, and wetland restoration are all examples of sustainable land management practices that help protect biodiversity and make the planet more resilient to weather extremes. Preserving natural areas lessens the toll the heatwave takes on plants and animals and makes ecosystems more robust in general.
Everyone has a role to play
Understanding the causes of Cerberus Heatwaves and their effects on wildfires is critical for developing effective prevention and mitigation plans. Importantly, resource allocation should prioritize the most vulnerable areas in order to ensure proper safeguarding and control. This is due to the fact that the impact of the Cerberus Heatwave-caused wildfires can be mitigated by investing in climate change mitigation and early detection and warning systems, which, if not allocated effectively, will leave other communities more vulnerable than others. Most importantly, citizens and the government must regard themselves as equal partners in this struggle. Citizens must follow professional body guidelines, and the government must be proactive in mitigating measures.
Found it interesting and would like more in the mail?