As the world grapples with the consequences of climate change, heat waves are becoming more frequent and intense. With Europe currently suffering from its own scorching heat wave, there is growing concern that the situation will deteriorate further in the future. Understanding the trends and implications of the European heat wave is critical for adapting and preparing for the challenges that lie ahead, especially as climate change becomes a more pressing issue. Will the heatwaves worsen in intensity and frequency? To answer this question, it is important to first understand what a heatwave is, what it means, what causes it, and what risks it poses.
Throwback to 2003…
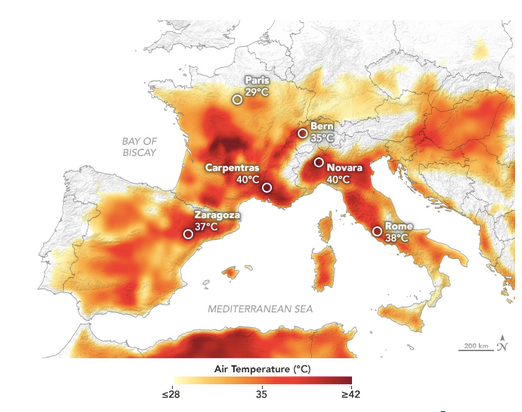
One of the most notable heatwaves in European history is the 2003 occurrence often referred to as the ‘European summer of heat.’ This event lasted from June to August and had devastating consequences, including the reported death of over 70,000 people. It was fuelled by a stationary anti-cyclone over Western Europe that held back rain-bearing depressions from the Atlantic and funneled hot and dry air from the Mediterranean. The heatwave led to record-breaking temperatures in the United Kingdom, France, and Switzerland, reaching 38.1°C, 40°C, and 41.5°C, respectively. Also, it had a severe impact on the elderly population, which according to UNISDR, France reported an estimated 14,802 casualties and Italy had over 4,000 in major cities during the month of August. The 2003 heatwave in Europe caught many countries unprepared, revealing weaknesses in their infrastructure and healthcare systems to handle extreme temperatures. In response, several implemented heat action plans and enhanced their heat alert systems to safeguard vulnerable populations during future heat waves. The event underscored the importance of improving preparedness through better heat action plans, early warning systems, and public awareness campaigns to protect those at risk.
…and the 2010 Russian heatwave
The summer of 2010 witnessed a devastating heatwave in Western Russia, Belarus, and Ukraine. This torrid weather was the worst in the 33 years prior, reported to cause an estimated 55,000 fatalities. The extreme heat and drought severely impacted crops, causing food shortages and economic losses. The Russian government faced criticism for its response to the crisis, leading to calls for better preparedness and heat mitigation strategies in the future. The event underpinned the importance of effective heat alert systems and support for vulnerable populations during extreme heat events. It also highlighted the need for early warning systems, coordinated response plans, and international collaboration to manage the impacts of such weather events. The heatwave was attributed to climate variability and weather patterns, prompting calls for improved urban planning, water management, and heat adaptation measures in the affected regions.
The 2019 episode…
In 2019, Europe encountered yet another notable heatwave. Record-breaking temperatures, surpassing 40 degrees Celsius, were observed in countries such as France, Germany, and the Netherlands. Specifically, the summer heatwave in Europe, particularly affecting France, Belgium, and the Netherlands, resulted in an excess mortality toll of 2,500 people when considered as a single event. The extreme heat impacted Western and Central Europe, with record-breaking temperatures affecting public health, agriculture, energy demand, transportation, and the economy. Unlike previous heatwaves, European governments displayed greater preparedness by issuing more effective heat warnings, building cooling centres, and providing information to vulnerable people.
Adaptation lessons for the future…
The effects of climate change are being felt all over the world, and Europe is not immune. Heat waves are expected to become more frequent and intense. Experts predict that there will be more extended periods of extremely high temperatures, which could have disastrous consequences. Analyzing previous European heatwave events has provided valuable insights into potential adaptation strategies. Implementing early warning systems and heat action plans, for example, as some European countries have done, can help mitigate the effects on vulnerable populations such as the elderly and young children. Green space in urban planning, efficient building design to reduce heat retention, and improved public transportation are all measures that can help to mitigate the urban heat island effect. Furthermore, addressing the threat of worsening heatwaves necessitates global collaboration. Governments, communities, and businesses must collaborate to cut greenhouse gas emissions, invest in renewable energy, and build climate-resilient infrastructure. Collaborative efforts can also be directed toward the preservation of natural ecosystems, which play an important role in regulating temperatures and preserving biodiversity.
As the world prepares for a future of increasing heatwaves, adaptation, and mitigation strategies will be critical. Europe can pave the way for a safer and more sustainable future by fostering collaboration, adopting sustainable practices, and prioritizing climate resilience to mitigate the worst effects of heatwaves and protect its people and environment.
Found it interesting and would like more in the mail?