In 2023, clean energy took on the front seat, driving China’s economic growth. China’s investment in clean energy sectors went up to an estimated 6.3 trillion yuan ($890 billion) from 4.6 trillion yuan in 2022 (A 1.7 trillion yuan (40%) increase). In the same year, the clean-energy sector made a significant economic impact in China, contributing approximately 11.4 trillion yuan ($1.6 trillion) when factoring in goods and services (a 30% surge compared to the previous year). As a result, the sector contributed over 9.0% of China’s GDP in 2023, compared to 7.2% in 2022. The implication of this was that an absence of the clean energy sector’s contribution to China’s economic expansion in 2023 would have resulted in a GDP growth of only 3.0%, falling short of the actual 5.2% growth recorded.
So, how did this remarkable growth occur? We will dig into the details in the coming paragraphs to understand how clean energy sectors spearheaded economic development in the country.
The Dominance of the “New Three”
When discussing the bedrock of the economic growth China experienced in the clean energy sector, the word “new three” emerges; that is—solar power, energy storage, and electric vehicles (EVs). This is in contrast to the “old three” – clothing, home appliances, and furniture. Let’s discuss the contributions of these sectors.
- Solar Power’s Unprecedented Growth
Solar power was a major driver behind the success of China’s clean energy revolution. The sub-sector experienced a rise in both investment and deployment. The Chinese government initiatives, such as the “whole-county distributed solar” and “clean energy base” programs, propelled the installation of solar panels to record levels. The Chinese dominance in solar manufacturing was underscored by the addition of significant production capacity, which drove exports and solidified the country’s position as a global leader in solar technology.
- Energy Storage
The energy service sector also experienced a remarkable surge, expanding to an estimated 0.6tn yuan in 2023, up from 0.5tn yuan in the previous year. China’s commitment to scaling up electricity storage capacity marks a significant stride towards a more flexible and resilient energy grid. Pumped hydro storage projects witnessed a dramatic increase, and investments in battery manufacturing capacity soared (This surge was in tandem with the proliferation of electric vehicles).
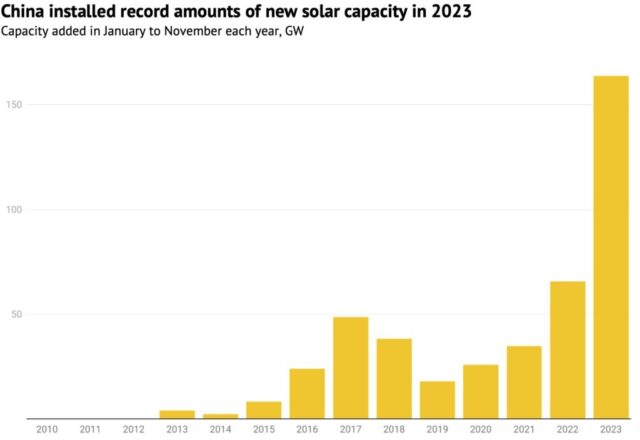
Source: Carbon Brief
With 167GW of pumped hydro capacity under construction and an additional 250GW in pre-construction stages, China is poised to enhance its grid’s ability to integrate variable renewable energy sources like wind and solar power. By leveraging pumped hydro storage, China aims to smooth out fluctuations in renewable energy generation and ensure reliable electricity supply.
- Electric Vehicles
Likewise, China’s electric vehicles grew in production and sales, soaring by 36% and 38%, respectively. This was also accompanied by a surge in EV charging infrastructure. Despite the phasing out of purchase subsidies, the EV market continued to thrive, signalling a shift towards market-driven demand. Domestically produced EVs also captured a significant market share, with China emerging as a global hub for electric vehicle manufacturing.
Investment in Energy Efficiency: Driving Sustainable Practices
Investment in energy efficiency accounts for about 60% of total investment, predominantly targeting industrial sectors. Industries face pressure to streamline processes and adopt more efficient technologies to meet stringent energy intensity reduction targets set by the government. This has catalysed significant investments in energy-efficient technologies and processes across various sectors.
Chinese investment in building energy efficiency amounts to 80 billion yuan annually. As part of the country’s 14th five-year plan, there’s a focus on energy savings in buildings and the development of “green buildings,” aiming for 80 million square metres per year of renovated and newly constructed green buildings.
The market for energy service companies (ESCOs) serves as a key indicator of investment in energy efficiency within industries and buildings. The market experienced steady growth, reaching an estimated 0.6tn yuan in 2023. China’s energy efficiency drive is reinforced by a suite of government policies and initiatives aimed at promoting sustainable practices. These initiatives provide a regulatory framework and incentives to encourage industries and businesses to invest in energy-efficient technologies and infrastructure.
China’s commitment to energy efficiency is not only about reducing environmental impact but also about driving sustainable economic growth. However, despite progress, challenges persist in scaling up energy efficiency investments. In 2022, a downturn in industrial energy service output was observed, influenced by sluggish industrial growth. However, the resilience of the building service sector highlights the potential for continued expansion. Addressing barriers such as upfront costs, technology adoption, and behavioural change will be critical to unlocking the full potential of energy efficiency investments.
Clean Energy’s Impact Beyond Economic Growth: A Global Perspective
Beyond driving economic growth, China’s clean energy push reverberates globally, shaping the trajectory of clean technology adoption and decarbonisation efforts worldwide. The impact extends across multiple dimensions, underscoring China’s pivotal role in the global energy transition.
- Lowering Global Prices and Accelerating Adoption
China’s unprecedented manufacturing boom in clean energy sectors has contributed to a significant reduction in global prices, particularly in solar panels and batteries. This steep decline in costs has democratised access to clean energy technologies, making them more affordable and accessible to nations worldwide. As prices continue to fall, the adoption of clean energy technologies is expected to accelerate, driving down global carbon emissions.
China’s dominance in clean energy supply chains solidifies its position as a global leader in clean technology manufacturing. The nation’s vast manufacturing capacity and export prowess have reshaped global markets, influencing the competitiveness of clean energy technologies. Other countries are now faced with the choice between leveraging China’s low-cost supply or investing in domestic production to diversify supply chains.
- International Cooperation and Climate Diplomacy
China’s clean energy investments and commitments signal its readiness to engage in international cooperation and climate diplomacy. China’s clean energy goals align with global efforts to mitigate climate change, such as the tripling of renewable energy capacity agreed upon at COP28. The Chinese government’s efforts to finance and develop clean energy projects overseas are expected to intensify, further driving global decarbonisation efforts.
Challenges Ahead
- Potential Oversupply
Despite the impressive growth of clean energy investments and infrastructure, concerns persist regarding the possibility of oversupply within the sector. This issue has the potential to disrupt market dynamics and investment viability.
- Market Saturation: As investment pours into cleanenergy projects, there is a risk of oversaturating the market with technologies like solar power and electric vehicles. Oversupply could lead to reduced profitability for companies and dampened investor enthusiasm, impacting future investment flows.
- Technological Innovation: Continuous innovation is essential to mitigate the risks of oversupply. Research and development efforts must focus on improving efficiency, reducing costs, and diversifying clean energy solutions to maintain competitiveness and stimulate demand.
- Threat of Trade Barriers
In addition to domestic challenges, China’s clean energy sector faces external pressures in the form of trade barriers and geopolitical tensions. These barriers could hinder market access, stifle innovation, and impede the global transition to renewable energy.
- Trade Disputes: Escalating trade disputes, particularly between major economies like China and the United States, threaten to disrupt the flow of clean energy products and technologies. Tariffs and other protectionist measures could raise costs for consumers and limit market expansion opportunities.
- Geopolitical Dynamics: Geopolitical tensions and competition for dominance in clean energy markets could further exacerbate trade barriers. Strategic considerations may influence policy decisions, leading to increased volatility and uncertainty for businesses operating in the sector.
Ensuring Sustainability and Resilience
Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach that balances economic growth with environmental sustainability and resilience. Policymakers, industry stakeholders, and international partners must collaborate to navigate the complexities of the clean energy transition effectively.
- Policy Coordination: Coherent and forward-thinking policies are essential to provide a conducive environment for clean energy investment and innovation. Government (Chinese inclusive) should prioritise regulatory certainty, incentivise research and development, and foster collaboration between the public and private sectors.
- International Cooperation: Mitigating trade barriers and geopolitical tensions necessitates diplomacy and cooperation on a global scale. Increased multilateral agreements can facilitate knowledge sharing, technology transfer, and collective action to accelerate the clean energy transition. With China’s leap in the clean energy race, the country can scale its impact beyond the shores of its borders.
- Investment in Resilience: Investing in resilience measures, such as diversifying clean energy portfolios and strengthening supply chains, can mitigate the impacts of potential oversupply and trade disruptions. Flexibility and adaptability are key attributes for navigating uncertainties in the evolving clean energy landscape.
Conclusion
In navigating these challenges and opportunities, China has the potential to further cement its position as a global leader in clean energy innovation, drive sustainable economic growth, and contribute significantly to addressing the pressing challenges of climate change and environmental degradation. Embracing a holistic approach that integrates economic, environmental, and social considerations will chart a course for the country toward a more sustainable and prosperous future for its citizens and the planet.
About CheckCarbonFact
CheckCarbonFact is a social accountability platform for promoting sustainability and responsible climate action by citizens, businesses and government. Read more about us here: https://checkcarbonfact.com/about/
Carbon Fact for the Day

Found it interesting and would like more in the mail?




