In November 2008, the UK made history by passing the Climate Change Act (2008), a groundbreaking piece of legislation that set a new standard for global climate action. With overwhelming bipartisan support, this act became the world’s first legally binding climate change mitigation target set by a nation.
Central to the Climate Change Act is the unequivocal requirement for the UK government to take decisive action to mitigate and adapt to climate change. The Act establishes a comprehensive framework for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and managing climate change risks, underscoring the UK’s commitment to global climate leadership.
Let’s delve into what this landmark legislation entails and its significance in shaping the UK’s approach to climate change.
Setting Ambitious Targets
At its core, the Climate Change Act mandates stringent emission reduction targets to combat climate change. Initially, the UK committed to reducing greenhouse gas emissions by 80% by 2050, compared to 1990 levels. However, in a bold move towards greater ambition, the UK revised its target in 2019, becoming the first major economy to commit to a ‘net zero‘ target. This updated goal requires the UK to achieve net zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050, signalling a resolute commitment to combating climate change on a global scale.
Key Pillars of the Act
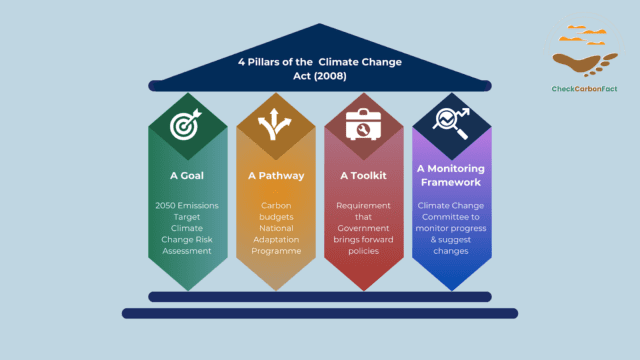
At its core are four fundamental pillars that provide a sturdy framework for climate action, setting a clear pathway towards a sustainable future. The four pillars of the UK Climate Change Act collectively form a blueprint for effective climate action, demonstrating the power of legislative leadership in addressing one of the most pressing challenges of our time.
Let’s explore each of these pillars and their significance in driving effective climate action:
-
Long-term Goal
At the heart of the Climate Change Act lies a bold and ambitious long-term goal to achieve net-zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050. This target, initially set to reduce emissions by at least 80% below 1990 levels, has since been updated to reflect the latest scientific evidence and the imperative of the 2015 UN Paris Agreement. By establishing a clear trajectory for emissions reductions, the Act provides a beacon of hope for a future free from the devastating impacts of climate change.
-
Pathway to the Goal:
Carbon budgets serve as critical milestones on the journey towards the long-term emissions target. Legislated over five-year periods, these budgets set legally binding limits on UK greenhouse gas emissions, providing a roadmap for incremental progress. By breaking down the overarching goal into manageable segments, the Act ensures accountability and fosters a sense of urgency in addressing climate change.
The UK so far has made tremendous progress in meeting its carbon budget, even though it faces some significant challenges. While the UK successfully met its first three carbon budgets, recent reports from the Climate Change Committee indicate challenges in meeting the fourth (2023–27) and fifth (2028–32) budgets. However, with the introduction of the sixth budget (2033–37) aligned with the net zero target, the UK is poised to recalibrate its approach towards achieving ambitious emission reduction goals.
-
Policy Framework:
Recognising that ambitious targets alone are not sufficient, the Climate Change Act mandates the development and implementation of robust policy programs to drive emissions reductions and address climate risks. This policy framework empowers the government to enact measures aimed at transitioning to a low-carbon economy, promoting renewable energy, enhancing energy efficiency, and fostering innovation across various sectors. By coupling ambitious goals with concrete policy actions, the Act catalyses tangible progress in the fight against climate change.
-
Independent Advisory Body:
Central to the Act’s effectiveness is the establishment of the Climate Change Committee (CCC) as an independent advisory body. Comprising experts with a diverse range of backgrounds, the CCC serves as a trusted source of guidance for policymakers, offering evidence-based recommendations on carbon budgets, climate risks, and mitigation strategies. By providing impartial analysis and monitoring progress, the CCC ensures that climate policy remains grounded in scientific rigour and best practices.
The CCC’s recommendations, including the landmark report advocating for the net zero target, have been instrumental in shaping the UK’s climate policy landscape and driving forward ambitious climate action.
Climate Change Risk Assessment and National Adaptation Programme
In addition to mitigation efforts, the Climate Change Act mandates regular assessments of climate change risks and opportunities through the UK Climate Change Risk Assessment (CCRA). This is published as a report, the last being in 2022. This comprehensive evaluation informs the development of a National Adaptation Programme (NAP), which outlines strategies to manage the impacts of climate change across various sectors. The latest programme, the Third National Adaptation Programme (NAP3), can be found on the UK Government website. By integrating adaptation into its climate policy framework, the UK demonstrates a holistic approach to climate resilience.
Responsibility and Collaboration
Achieving the ambitious goals of the Climate Change Act requires the government to prioritise robust collaboration across boards, such as departments and devolved administrations, to address the multifaceted challenges posed by climate change. Some critical collaborative opportunities include:
Integrated Decision-Making
At the heart of the Climate Change Act is the recognition that tackling climate change requires a coordinated approach across government departments. The establishment of the Cabinet Committee on Climate Change, chaired by the Prime Minister, is an actualisation of this, spotlighting the government’s commitment to integrated decision-making at the highest levels. The CCC is supported by subcommittees to ensure that climate change considerations are mainstreamed into policy decisions across various sectors of government.
Departmental Responsibilities
Key government departments, such as the Department for Energy Security and Net Zero (DESNZ) and the Department for Environment and Rural Affairs (DEFRA), play pivotal roles in driving climate policy and adaptation efforts. DESNZ takes the lead in developing policies aimed at reducing emissions, while DEFRA spearheads domestic adaptation initiatives. By delineating clear responsibilities and fostering collaboration between departments, the UK government ensures a cohesive and holistic approach to addressing climate change.
Collaboration with Devolved Administrations
In addition to collaboration within the UK government, the Climate Change Act recognises the importance of engaging with devolved administrations in Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland. While the Act applies across the UK, devolved administrations have the autonomy to develop their own climate change policies tailored to their unique circumstances. This collaborative approach ensures that climate action is contextually relevant and responsive to the specific needs and priorities of each region.
Stakeholder Engagement
Beyond government collaboration, the Climate Change Act also emphasises the importance of engaging stakeholders from civil society, academia, and the private sector. By fostering dialogue and partnerships with diverse stakeholders, the UK government can leverage collective expertise and resources to drive meaningful climate action. This inclusive approach ensures that climate policies are informed by a wide range of perspectives and priorities, enhancing their effectiveness and legitimacy.
Successes and Challenges
The UK Climate Change Act has undeniably achieved significant successes since its inception. The Act is widely acknowledged as a significant factor in the ongoing decrease of the UK’s greenhouse gas emissions, which had dropped by 41% below 1990 levels by 2019. This achievement underscores the Act’s efficacy in driving tangible environmental progress while simultaneously nurturing economic growth, with the UK economy expanding by 78% over the same period.
However, amid these successes, challenges remain. While the Act has been effective in driving mitigation efforts, progress on adaptation has been slower. Despite the Act’s mandate for regular assessments of climate risks and the development of adaptation strategies, the implementation of these policies has often been overshadowed by mitigation priorities. This disparity highlights the need for a more balanced approach to climate action, with equal emphasis on both adaptation and mitigation measures.
Furthermore, the Act’s framework has faced challenges in the absence of clear timelines for government policy development, which has led to delays in the introduction of crucial measures. This has hindered swift action on climate change. Additionally, uncertainties surrounding the treatment of emissions from international aviation and shipping have posed significant hurdles in aligning climate targets with international commitments.
Looking Ahead
As the UK charts a course towards achieving its net zero targets and confronts the complex challenges of climate change, the lessons learned from the Climate Change Act will continue to guide future endeavours. By prioritising evidence-based policy, fostering collaboration across sectors, and embracing ambitious targets, the UK is poised to lead the charge in global climate action.
Looking ahead, the next decade will present a new set of challenges and opportunities for UK climate policy. Achieving net-zero emissions by 2050 will require concerted efforts across all sectors of the economy, accompanied by greater public engagement and social equity considerations. Building on the Act’s foundation, future climate legislation must prioritise inclusivity, resilience, and innovation to navigate the complex challenges of a rapidly changing climate.
About CheckCarbonFact
CheckCarbonFact is a social accountability platform for promoting sustainability and responsible climate action by citizens, businesses and government. Read more about us here: https://checkcarbonfact.com/about/
Carbon Fact for the Day

Found it interesting and would like more in the mail?




